Difference between revisions of "Consonant (definition)"
Kmccullough (talk | contribs) m |
Kmccullough (talk | contribs) m |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[File:IPA consonants.gif|thumb|right|https://www.internationalphoneticalphabet.org/ipa-charts/consonants/]] | |
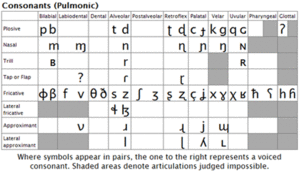
| + | Phonetically, '''consonants (C)''' are sounds that involves a significant occlusion (closure or constriction) of the vocal tract. These sounds are traditionally characterized by voicing, place of articulation, and manner of articulation features; these are listed below and illustrated in the graphic to the right. | ||
| − | For a complete description of Gaelic consonants and its phoneme inventory, see the main article at [[Sounds of Scottish Gaelic]]. | + | #Voicing (+voice, -voice) |
| + | #Place (labial, labiodental, dental, alveolar, postalveolar, palatal, retroflex, velar, uvular, pharyngeal, glottal) | ||
| + | #Manner (plosive, nasal, trill, tap, fricative, aproximant) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Such features are used to distinguish between consonantal segments and define natural classes (e.g. continuant, coronal, etc.). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Consonants help define the phonotactics of a language acting as onsets, codas, and occasionally nuclei of syllables. Consonants contrast with vowels which are articulated with an unobstructed vocal tract. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''For a complete description of Gaelic consonants and its phoneme inventory, see the main article at [[Sounds of Scottish Gaelic]].'' | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| + | *[[Sounds of Scottish Gaelic]] | ||
*[[Vowel (definition)]] | *[[Vowel (definition)]] | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| + | *[http://www.paulmeier.com/ipa/charts.html Interactive IPA Charts] | ||
*http://akerbeltz.org/index.php?title=Consonants | *http://akerbeltz.org/index.php?title=Consonants | ||
| + | The link below takes you away from the Gaelic Wiki to Wikipedia. Since wikipedia pages can be edited by anyone, they often contain inaccurate information. So be careful! | ||
*http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consonant | *http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consonant | ||
Latest revision as of 20:06, 25 October 2020
Phonetically, consonants (C) are sounds that involves a significant occlusion (closure or constriction) of the vocal tract. These sounds are traditionally characterized by voicing, place of articulation, and manner of articulation features; these are listed below and illustrated in the graphic to the right.
- Voicing (+voice, -voice)
- Place (labial, labiodental, dental, alveolar, postalveolar, palatal, retroflex, velar, uvular, pharyngeal, glottal)
- Manner (plosive, nasal, trill, tap, fricative, aproximant)
Such features are used to distinguish between consonantal segments and define natural classes (e.g. continuant, coronal, etc.).
Consonants help define the phonotactics of a language acting as onsets, codas, and occasionally nuclei of syllables. Consonants contrast with vowels which are articulated with an unobstructed vocal tract.
For a complete description of Gaelic consonants and its phoneme inventory, see the main article at Sounds of Scottish Gaelic.
See Also
External Links
The link below takes you away from the Gaelic Wiki to Wikipedia. Since wikipedia pages can be edited by anyone, they often contain inaccurate information. So be careful!
References
- Crystal, D. (2008) Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics. 6th Edition. Wiley-Blackwell.
- Ladefoged, D. (2010) A Course in Phonetics. 6th Edition. Wadsworth Publishing.
- Matthews, P. H. (1997) The Concise Oxford Dictionary of Linguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press.